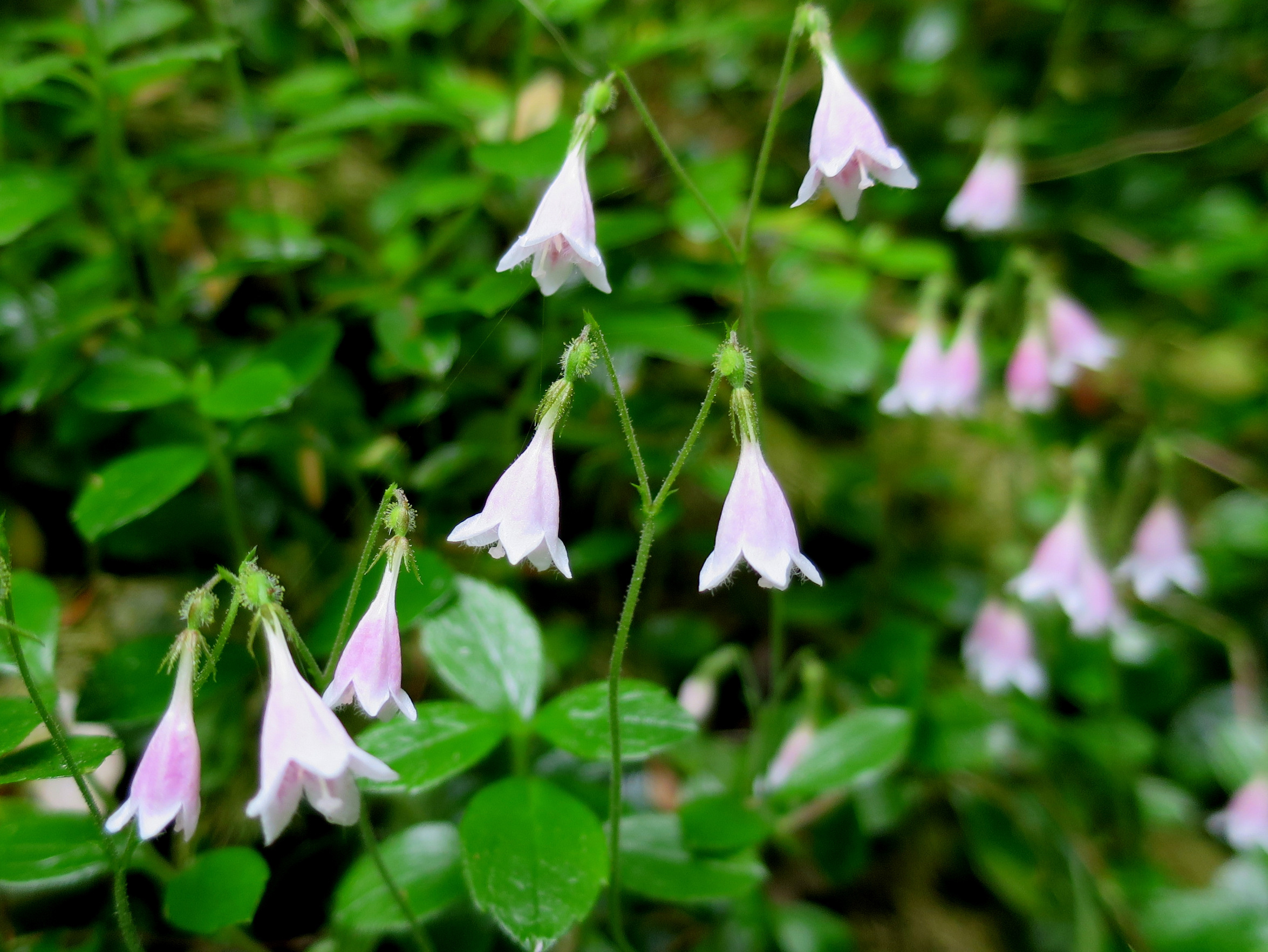
Linnaea borealis
twin flower
Habit: a delicate evergreen perennial with trailing vine stems, up to 3 feet long. The semi-woody stems freely root where they touche the ground, usually forming thick mats. Small, firm and shiny leaves grow oppositely along the vines. Each leaf is up to 1 inch long, broadly elliptic to rounded and typically presents shallow teeth along the upper half. A pair of nodding, trumpet-like flowers with lobed pink corollas grow at the tip of a forked flowering stalk. The flowers are fragrant and bloom from early summer to early fall. Its tiny nut-like fruit bear a single seed and are equipped with hooked bristles which are easily caught on the fur of small mammals and feather of birds.
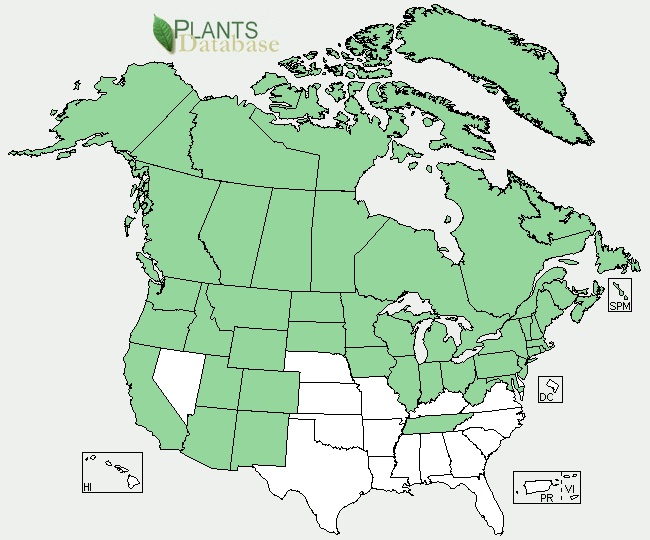
Ecology: inhabits shady, mossy forests or open woods in wet to dry locations at low to fairly high elevations. It is widespread throughout most of the circumboreal lands and higher latitudes of North America, from the Pacific Northwest through the Rocky mountains and Great Lakes, yet its native habitat reaches as far south as California, New Mexico and Tennessee to the east.
Growing conditions: enjoys full shade to dappled light, and moist to rather dry soils. Beautiful as a ground cover in the understory of conifers and taller shrubs, or trailing over a fallen tree. The plant tends to spread quickly but not aggressively.
The scientific name Linneae was chosen in honor of Carl Linnaeus, a Swedish botanist and physician known as the Father of Taxonomy. Linneae boreallis was reportedly his favorite flower and is the only plant in the genus. The species epithet borealis refers to the plants northern geographic distribution.
Specs
Herbaceous Perennial
2-6 inches (5-15 cm)
1-5 feet (0.3-1.5 m)
3a to 8b