Betula occidentalis
water birch
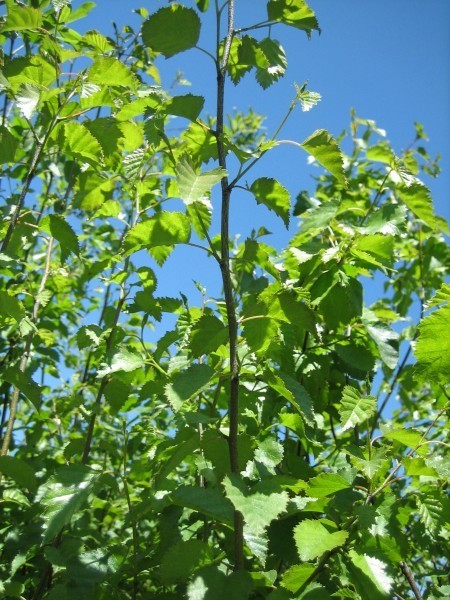
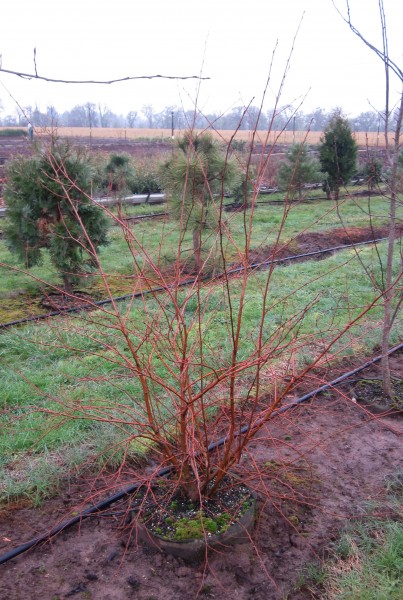
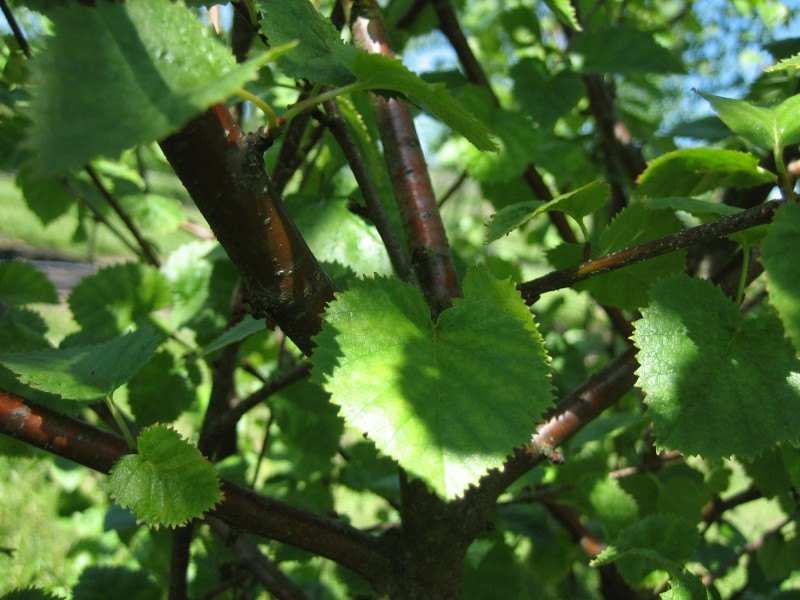
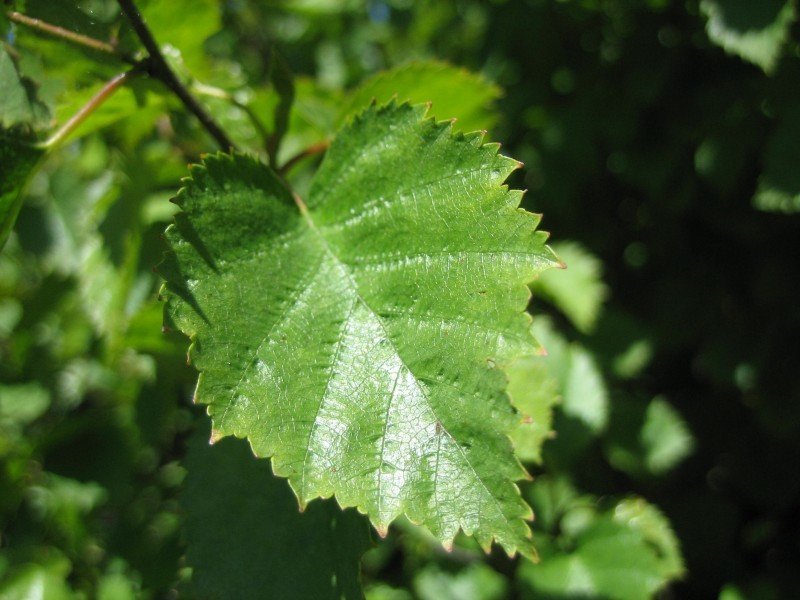
Habit: commonly a large multi stemmed shrub with several spreading trunks and a rounded crown of spreading and drooping branches, usually forming clumps or thickets. The coarsely toothed leaves are dark green above and pale yellow-green beneath becoming dull yellow in fall. The bark is thin, bronze or cherry red, smooth and does not peel. The flowers are wind-pollinated catkins, the male catkins pendulous, and female catkins erect. The fruit is composed of numerous tiny winged seeds packed between the male catkin bracts. The red color of the branches and twigs create the same winter effect as red twigged dogwoods.
Ecology: water birch is typically a riparian plant, occurring almost exclusively along streams in mountain canyons, usually in coniferous forests, or mountain slopes 200-8000 ft (61-2400 m) elevation where streams drain snowmelt.
Growing Conditions: full sun to part shade and nutrient-rich moist to wet soils; very flood tolerant.
Water birch is used in forested riparian buffers to help reduce stream bank erosion and provides important habitat for many birds and other animals. The catkins, buds, and seeds are eaten by numerous bird species; hummingbird and red-naped sapsucker feed on sap oozing from holes in the bark made by sapsuckers.
Specs
Deciduous Tree/Shrub
10-30 ft (3-9m)
6-12 ft (2-4m)
5-10